The nature of the development of this type of alopecia is closely related to sex hormones and hereditary factors. Thinning and hair loss is triggered by the sensitivity of hair follicles to dihydrotestosterone, which is transmitted genetically. Under the influence of this hormone, a spasm occurs in the hair follicles. As a result, dystrophy of the hair follicle develops, most of the follicles die.
A characteristic manifestation of androgenetic alopecia is the absence of hair in the area of the forehead and crown and the continued growth of hair in other places that are insensitive to sex hormones.
There are 3 types of androgenetic alopecia:
- Horseshoe. The clinical picture is manifested in excessive hair loss of the frontal part of the temples. Further, the process expands throughout the fronto-parietal part, gradually forming a bald spot that looks like a horseshoe.
- Nest. The coat begins to thin in the forehead area. Gradually, the process captures the parietal zone, forming a bald spot that resembles a nest.
- Mixed type. Hair at the same time thinning in the fronto-parietal part and on the crown of the head. There are temples in the shape of the letter M. If the process is not stopped, baldness flows into the type of horseshoe.

This type of alopecia is most often diagnosed in women, as a result of hormonal adjustment of the body during pregnancy, lactation or puberty. For diffuse baldness is characterized by uniform hair loss over the entire surface of the head.
Note! Also provoke the development of diffuse alopecia can nervous strain, use of narcotic drugs, uncontrolled intake of antibiotics and pill contraceptives.
Diffuse alopecia is divided into two subspecies:
- anagenovuyu (proceeds during the period of active growth of hair),
- telogen (diagnosed in the complete rest phase of the follicle).

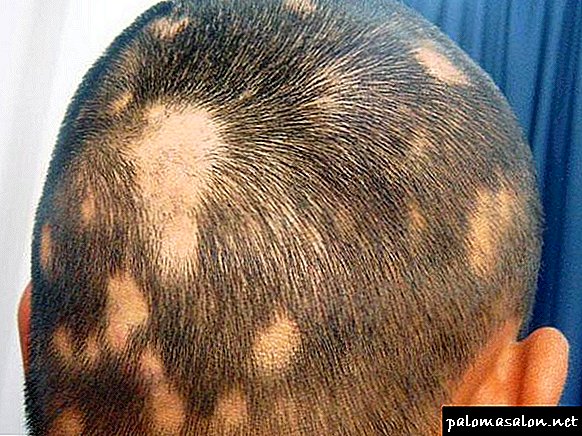
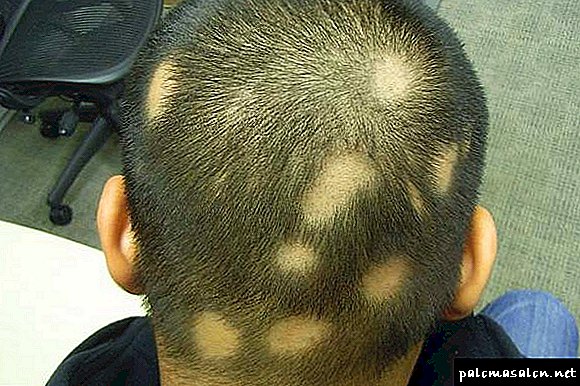
Abundant local hair loss is diagnosed as focal or nesting alopecia. A prominent feature of this type of baldness is the roundish or oval shape of the hairline.
The process of hair loss with focal alopecia goes through three stages:
- Progressive - the centers of baldness are actively expanding, gradually merging with each other.
- Stationary - hair loss stops.
- Regressive - healthy hair growth is restored.
A long-term state of stress, head injury, an imbalance of hormones in the body, and diseases of an autoimmune nature can provoke the development of focal alopecia.
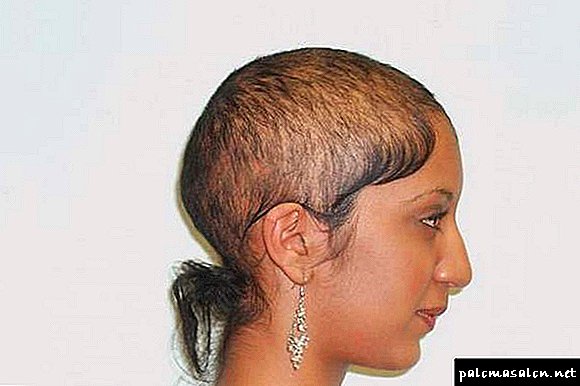
Irreversible process of hair loss, accompanied by severe inflammatory, atrophic and cicatricial processes diagnosed as cicatricial alopecia. The factors that provoke the development of this type of baldness are: diseases of an autoimmune nature, infections of the skin, genetic predisposition.
In cicatricial alopecia, hair follicles are destroyed, in place of which scars appear. These seals connective tissue completely arrest the growth of new hair.
Attention! The clinical picture of cicatricial alopecia appears in asymmetric foci of prolapse, which show scars and atrophic lesions. In the center of these areas remains a few healthy hair.
There are the following forms of cicatricial alopecia:
- secondary - develops as a result of any disease,
- X-ray - develops after an X-ray study of mycosis of the skin,
- idiopathic - is extremely rare, has an unclear nature of development.

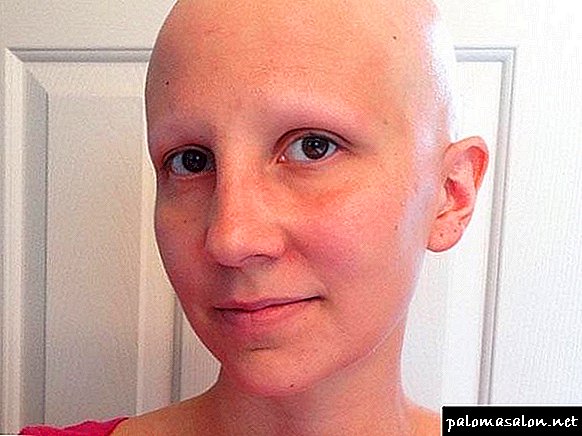
This type of alopecia is characterized by complete baldness, not only of the head, but also of other parts of the body (arms, legs, genital area, eyebrows and eyelashes). Total alopecia develops rapidly. Within two months from the beginning of the fallout, very large bare areas are formed, merging with each other.
It provokes the process of active hair loss a prolonged state of stress, hormonal disruptions, fungal lesions of the skin, exposure to radioactive and chemical substances, uncontrolled antibiotics, chemotherapy, head injuries.
There are alopecia:
- total - loss of hair all over the body,
- subtotal - develop more slowly, affect only the guard hair on the head,
- universal - the pathological process of baldness affects the whole body, the nail plate becomes thinner.

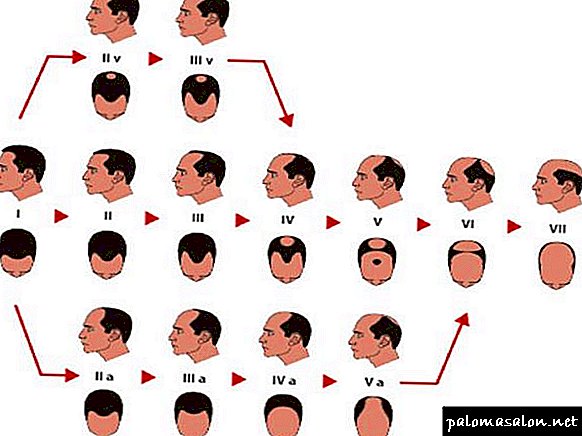
Stages and degrees of baldness according to Norwood
Before you designate a course of treatment for alopecia, the doctor trichologist determines the degree of hair loss. For this purpose, the Norwood scale is used - a table with pictures and a detailed description of the severity of hair loss. The Norwood scale combines all existing types of alopecia.
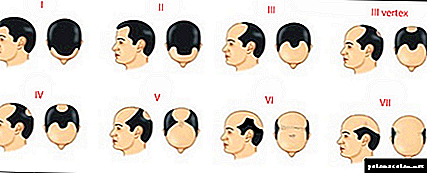
The classification of baldness according to Norwood includes seven degrees of male alopecia:
- Initial stage. Manifested by loss of hair from the front, temporal and frontal region of the head.
- The second. Small bald areas in the area of the forehead and temples move a few centimeters towards the back of the head. As a result, the temporal and frontal parts take the form of a triangle. The scalp of the parietal region of the head.
- Third. The area of the temples and forehead thins even more, pronounced bald patches appear, advancing more than 2 cm from the frontal line.
- BEHIND. Crown alopecia, which is characterized by active hair loss on the crown. Most often, the degree of baldness 3A develops in men after forty-five years.
- Fourth. In the parietal zone, the hair is thinning even more or almost everything falls out. The area of temples and forehead becomes bare. Parietal and fronto-temporal zones are separated by a strip of hair.
- Fifth The scalp on the top almost disappeared. Forehead and temples bare even more. The balding process covers a large part of the head, forming a horseshoe-shaped hairline.
- The sixth. The hair that connects the frontal and crown areas earlier falls out. As a result, a large magnitude bald spot is formed.
- Seventh. Complete loss of the front and back of the head of the hair. A small part of the hair remains only in the area of the ears, neck and neck.
Only careful attention to yourself and diagnosis of alopecia at the initial stage will allow you to quickly eliminate the problem and avoid complete baldness.
Useful videos
Types of baldness: gnezdny, androgenic (androgenetic), cicatricial, focal, diffuse, total.
Types of baldness (alopecia) on the head, beard, eyebrows, eyelashes. Balding scale.
Stage of the disease

- The first stage is characterized by thinning of hair in the front of the head, that is, from the temporal and frontal areas.
- The second stage - there are noticeable bald patches that, starting from the frontal-temporal region, are sent to the back of the head. They have a clear view of the triangles.
- The third stage - the hair in the temporal and frontal parts becomes even smaller, besides this begins baldness at the crown.
- The fourth stage - severe hair loss on the parietal part of the head, while the frontal area and temples are almost completely bare.
- Fifth stage - the frontal line of the scalp is significantly shifted top, parietal part becomes bare. At this stage, the scalp takes the form of a horseshoe.
- The sixth stage is pronounced baldness in front, behind and on the sides of the head. The exposed areas merge into one huge bald spot, a thin sparse strip of hair in the shape of a horseshoe remains.
- The seventh stage - you can observe a small amount of hair above the ears and in the neck area, and the total loss of the whole head of hair is not excluded.
Usually all stages of baldness in men occur very quickly. In most cases, the whole process takes place within 15 years, but it happens and this is when complete baldness occurs within 5 years.
Alopecia in women progresses much more slowly than in men. Complete loss of hair is not peculiar to the female sex, but a pronounced thinning and deterioration of the hair structure is possible. There are 3 stages of hair loss in women:
- The first stage is a moderate barely noticeable thinning of the hair along the center line of the parting, starting from the frontal zone to the top. Visually reducing the amount of hair is not so critical.
- The second stage - there is an active loss on the parietal region and the parting becomes wider. Due to progressive hair loss, the exposed areas expand and the scalp becomes visible.
- The third stage - there is complete baldness of the parietal lobe. However, in other areas new hair may grow, but their structure may deteriorate.
Female pattern baldness is caused by damage to any part of the scalp. This is usually seen by the central or side parting.
- congenital anomalies or pathological development of hair follicles (ichthyosis, pigment incontinence),
- infectious diseases (leprosy, leishmaniasis, syphilis),
- physical factors (radiation, too high and low temperatures, acids, mechanical trauma),
- skin cancer,
- systemic diseases (scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis),
- lichen planus

Non-scarlet
- genetic predisposition
- immune and autoimmune disorders,
- endocrine and metabolic disorders
- insufficient blood supply to the scalp and face,
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine,
- diseases of the digestive tract,
- strong long-term stress, which entails a spasm of blood vessels and malnutrition of hair follicles,
- some medications
- effects on the body of industrial or household chemicals, as well as exposure.
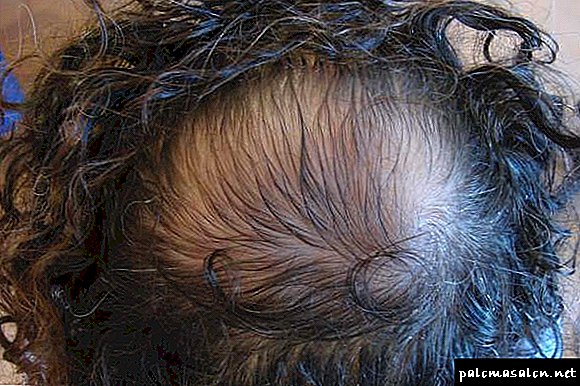
Non-cicatrical alopecia, in turn, is divided into subspecies. These include:
1. Androgenetic alopecia. It is considered the most common form of this disease. Baldness of this type occurs due to the fact that the male hormone testosterone is converted to dihydrotestosterone. Increasing this hormone has a direct effect on the hair follicles, that is, their timely feeding stops and subsequently they die off. As a result, in the process of washing and combing the hair falls out strongly, becoming brittle and lifeless. New hair grow weak and dull. This unhealthy process proceeds very quickly, which soon leads to the appearance of baldness on the head.
You can list risk factors that further aggravate the main cause of androgenetic alopecia. This includes:
- hormonal disruptions in the endocrine system,
- lack of balanced nutrition
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body,
- stresses and emotional overvoltages that pose a threat to health,
- taking some medication.
- Local - areas without hair occur in any areas of the head and they do not connect with each other.
- Ribbon or serpentine - the center of baldness takes the form of a tape that goes on the sides of the head from the temples to the back of the head.
- Subtotal - is characterized by gradual baldness with the formation of small foci, which later merge into large ones. This form also has a loss of eyelashes and eyebrows.
- Total - baldness occurs with lightning speed (2-3 months). Hair fall on all parts of the body, including eyelashes and eyebrows.
- Ringworm - means breaking the hair in the pathological focus at the level of 1-2 cm.
- Marginal - unhealthy lesions occur along the edges of the scalp. This is the back of the head and the temples area.
- Naked - manifested by extensive foci of baldness with rare preservation of individual strands.
- Universal - hair loss throughout the body, occurring over the years.
In this video, the trichologist Kotova I. tells about the nesting type of alopecia, its manifestations and causes:
If nesting alopecia has a benign etiology, it proceeds in 3 stages:
- progressive - increased hair loss within 5-6 months. There may be some symptoms of inflammation - redness, itching, burning, tingling,
- inpatient - remission of symptoms and stop hair loss,
- regressive - new hair growth is observed.
The speed and volume of hair loss depends on many factors:
- selection and dosage of medicines,
- duration and frequency of chemotherapy courses,
- the age of the patient and the structure of the hair.
Restoring the habitual hair will not be earlier than 3-6 months after treatment. It is important to note that many patients may subsequently change the quality and type of hair.
Diagnostics
- The study of hormonal background (tests for thyroid hormones).
- A blood test to determine the parameters of the immune system, as well as iron-containing elements.
- Trichogram, phototrichogram - study of the skin, including the amount of hair and their structure, the diameter of the hair shaft and the bulbs.
- Diagnostic test for stretching hair. Gently without effort pull the curls and with a positive hair sample easily falls.
- Detailed study of the structure of the hair under the microscope.
- Scalp biopsy.
Definitely, not all diagnostic methods are used immediately. After examining the scalp and clarifying complaints, the trichologist directs him to the necessary diagnostic procedures, and then selects the appropriate treatment based on the results obtained.

Drug therapy
- Drugs that improve blood circulation - Curantil, Solcoseryl, Actovegin.
- Hair growth biostimulants - Minoxidil, Tricomin.
- Preparations containing zinc and vitamins A, E, H and group B.
- Immunomodulators - Levamisole, Inosyplex, Echinacea.
- Sedatives - Persen, Novopassit.
- Hormonal drugs - Prednisolone, oral contraceptives for women, glucorticoid ointments.
Folk remedies
There are a great many proven recipes for hair loss. Here are some of them:
- Burdock mask. You must take 30 ml of burdock oil and add 50 grams of dry mustard powder to it. Mix everything and apply to the scalp abundantly rubbing the mixture. Leave on for 20 minutes and then rinse with warm water. You can use this mask once a week.
- Garlic-honey mask. Take 1 tbsp. l chopped garlic and 1 tbsp. l honey Stir and rub into the hair roots. Leave the composition for 20-30 minutes, and after a time rinse with cool water.
- Beer mask In 250-300 ml of beer at room temperature, add 2 chicken yolks. Stir well until a uniform consistency and apply to the hair, not forgetting the roots. Leave for 30 minutes and then rinse off.
- Honey-lemon mix. For this mask will require 1 tbsp. l honey, 1-2 tbsp. l lemon juice and 1 egg yolk. All components need to be mixed until a homogeneous mass and apply the mixture on clean hair. Wrap your head with a warm towel and walk with this composition for an hour. To enhance the effect, you can add 1 spoon of pepper tincture. At the end of time, rinse with warm water.
- Onion mask. Grind 2 onions to a mushy state and add 1 spoon of honey. Mix everything thoroughly, apply the mixture to your hair and hold it for 30-40 minutes. Then rinse with warm water.
In order to obtain the desired effect of hair growth masks, it is necessary to do them regularly and alternate among themselves. From the choice of one recipe and a single application of the result will not be.

Prevention
- In the cold season, namely on frosty days wear a hat. The same applies to very hot days when a long stay in the sun requires a headdress.
- Do not get involved in the use of hair dryers, curling irons, hot irons, hair curlers.
- Do not abuse frequent staining, perm and similar procedures.
- Have a comb with natural bristles and no sharp teeth.
- Periodically indulge your hair with vegetable masks, decoctions, infusions.
- Follow the diet.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Treat all available diseases.
Compliance with these simple recommendations will keep your hair healthy and strong. It is better not to engage in self-treatment, as this can be harmful and miss valuable time. If you have any doubts, you should contact the trichologist to prevent the disease and take action in time.
Briefly about interesting
Despite the fact that the existing classification is known as the Norwood Baldness Scale, in fact Hamilton is rightly considered its founder. The degree of baldness was developed by him in the early 50s of the last century, and only 20 years later, they were changed and supplemented by Dr. Otar Norwood. Therefore, sometimes in the literature we find the degree of baldness on the Hamilton-Norwood scale.
Why do men start to go bald?
According to scientists, the most common factors that cause hair loss in men are:
- Age changes at which the full nutrition of hair stops. The bulbs are much weaker, the hair begins to fall. With age, baldness concerns not only the frontal and temporal parts of the head, but also the occipital and parietal parts. Unfortunately, stopping such a process is extremely difficult.
- Genetic predisposition. Unfortunately, many representatives of the strong half of humanity have genetically hair loss. Surprisingly, under the influence of hormones, men, like women, can lose hair. The cause of baldness in this case is the hormone dihydrotestosterone. The effect of the hormone also affects the state of the strands: the hair becomes dry, colorless, thin and weakened, falls out, and new ones do not grow.
Norwood Alopecia
Trichologists usually classify male type of baldness according to the Hamilton-Norwood method. In diagnostics, special diagrams are used, which determine the degree of strand loss.
For the first time such a classification was developed in the middle of the 20th century by a dermatologist Hamilton, and in the 1970s, it was slightly modified by Dr. Norwood. The second scientist added several stages of baldness to the original classification. To date, the scale includes seven degrees of baldness in patients with different subtypes, and it is used by trichologists to diagnose the problem of the patient.
Consider all the degrees of male baldness according to Norwood.
- 1 degree baldness. Normal front hairline and a slight backward shift are observed. The minimum recess along the front line of the hair, as a rule, is not noticeable to others and is detected only when examined by a trichologist.
- 2 degree baldness. For the second phase, according to Norwood, the so-called triangle shape is distinguished by the front line of hair growth. As a rule, this form is symmetrical and covers an area of not more than 2 cm from the front line of hair growth.
- 3 degree. This phase of baldness is characterized by a symmetrical thinning of the strands at the temples. It is possible both their partial covering with hair, and complete baldness in this zone. Halves can extend further than 2 centimeters.
- 3 parietal power. Loss of strands falls on the parietal zone. This stage is characterized by moderate thinning of the front line of hair. The density of the front line in the temples with more than the previous degree.
- 4 degree. Baldness in the anterior temporal zone becomes more pronounced than in 3 degrees. On the crown there are sparse hairs or their absence. Usually in the fourth stage of baldness, two areas of hair loss are separated by a strip of moderately thick strands that runs along the top of the head. The strip is usually connected to the side zones of the head.
- 5 degree. In this case, the parietal zone of baldness remains separated from the anterior-temporal region, but to a lesser extent. On the crown there is a lack of hair or very rare strands. And at the top of the hair are becoming more thin and rare. The pre-temporal and parietal zones increase in size. The sides of the hair also thin and form a horseshoe-shaped form behind the head.
- 6 degree. Through the apex, between the lateral sides of the head, thin sparse hairs remain. The parietal and anterior-temporal zones constitute a single figure and are not separated, the area of hair thinning increases.
- 7 degree. The most serious degree of baldness, according to the classification of Hamilton-Norwood. In this phase, the horseshoe-shaped zone of alopecia becomes final, the lateral and parietal areas thin out even more. Hair actively fall out on the back of the head, above the ears. Hair remains on the lateral surfaces of the head, dropping below the occiput.
In addition to the classification of Hamilton-Norwood, there are three main types of baldness:
- Type "Horseshoe". Baldness begins with the frontal lobe and descends closer to the temples. Then it goes over to the entire fronto-parietal zone, forming a hair loss site resembling a horseshoe.
- Type "Nest". Lots of baldness occur in different areas of the head, chaotically, a nest-like area appears on the crown. This form of hair loss sooner or later takes the form of a horseshoe.
- Mixed type. Hair falls out at the same time both on the temples and in the parietal zone.
How to treat male pattern baldness?
In fact, it is possible and necessary to treat baldness. The main thing is to contact an experienced trichologist and find the best way to eliminate an unaesthetic problem.
All treatment options can be presented in three main groups:
- Drug treatment. The trichologist prescribes tests for the man and, by their results, determines the appropriate drugs. As a rule, the doctor prescribes a course that includes drugs based on Minoxidil - hair growth stimulant. Highly effective drug is spray ALERANA®. According to clinical studies: increased hair loss stops after 6 weeks of spray application in 87% of cases.
- Hair transplantation is considered one of the most effective procedures for any degree of baldness. The hair is transplanted from the “donor zone” to the alopecia site. Transplantation can be performed by surgical and non-surgical methods.
- HFE hair transplant is a modern procedure for hair transplantation using a microneedle. It is considered the most progressive way to transfer strands.
For those who want to strengthen the hair, make the strands thick and strong, we also recommend trying Alerana shampoo for men growth activator.
 Where can one buy
Where can one buy
This tool for nourishing and strengthening hair contains extracts that normalize the work of the sebaceous glands, prevent dandruff and heal the scalp.
The active ingredients of the shampoo are:
- tea tree oil that prevents hair loss,
- sage extract and rosemary oil, normalizing the activity of the sebaceous glands,
- chestnut and ginseng extracts toning the scalp and activating blood circulation,
- burdock extract, which stops the hair loss process and promotes the growth of new strands,
- Niacinamide, which stimulates the microcirculation of blood, improves nutrition, nourishes the follicles with oxygen and moisturizes the scalp.
So now you know a lot about Norwood baldness and you can determine how serious your problem is. Do not postpone the visit to the doctor, treat your health carefully, and thick strong curls will delight you for a very long time.
Latest posts
The course on moisturizing: an overview of hair moisturizers
To moisturize dry and damaged hair, will have to try. Fortunately, with modern makeup cosmetics nothing is impossible. If a
Hair Sprays - Express Moisturizing Format
When the hair needs to be moisturized, there is no doubt. Dry, damaged, poorly stackable and dull - all these are signs of lack
Whey - what is it
Active hydration in action! Dry hair serum - beauty-tool with a healing effect. Let's talk about how it works, from what
Moisturizing in a square: balms for dry hair
Moisturizing balm designed for dry hair. Within a couple of minutes after application, the hair is smoothed out, becoming more elastic. With
Moisturizing hair mask - essential
Dry hair requires special care. Moisturizing masks that nourish the scalp and fill the hair will help restore the structure and revitalize the strands.
Goodbye dryness! Moisturizing hair shampoos
Dry strands are not a reason for sadness, but a reason for action! An integrated approach begins with the selection of a good shampoo. Tell you what the "trick" moisturizers
Causes and differences in men and women
Main The reasons contributing to the occurrence of this disease are:
- hormonal disorders in the body (during pregnancy, breastfeeding, with diseases of the endocrine system, etc.),
- iron deficiency in the body
- damage to the scalp with various fungal diseases,
- systematic stress and malfunction of the nervous system,
- action of medications (contraceptives, hormone-based drugs, etc.),
- regular supercooling of the head,
- radiation exposure, etc.
Comparing the stages of baldness in women and men, we can note their significant difference. The classification of the stages of female pattern baldness is simpler and includes only three stages. Moreover, cases when a woman shows the last degree of baldness are extremely rare.
Stages Norwood
 Most doctors use the Norwood classification, developed in 1970, to determine the degree of baldness in men. In total, this classification includes 7 stages of manifestation of alopecia. Consider them in detail:
Most doctors use the Norwood classification, developed in 1970, to determine the degree of baldness in men. In total, this classification includes 7 stages of manifestation of alopecia. Consider them in detail:
- Stage I - is the beginning of the disease and is characterized by small bald patches that appear along the front line of hair growth (in the form of triangles). It is characteristic of the day of the youngest male representatives (18-25 years old).
As a rule, at this stage, rarely anyone pays attention to the process of baldness that has begun, and accordingly no measures are taken.
It should be noted that in this situation, the measures listed above will no longer have an effect. It is necessary to do a hair transplant. VII stage - all head bald. It remains only a narrow strip of hair, stretching from ear to ear along the back of the head.
This stage is the most serious, and usually in this case, no means will not help, even a hair transplant, since the material for this procedure no longer remains. The only solution in this situation is to wear a wig.
The sooner a man sees the first signs of baldness, the more money he can use to combat this disease.
Measures to combat hair loss
 So, at stages 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5, the following methods are used to combat baldness:
So, at stages 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5, the following methods are used to combat baldness:
- cosmetics (shampoos, lotions, balms),
- special preparationspromoting hair growth (for example, dimexide, nicotinic acid, d-panthenol, etc.),
- injections into the scalp,
- and traditional medicine (tinctures, masks, etc.).
Besides, men, it is important to adhere to proper nutrition, which will be able to saturate the body with all the necessary trace elements. Also, it will not be superfluous to drink a course of vitamins that will strengthen the body and try to avoid stress.
Regressive process
In some cases, regression of alopecia may occur. This phenomenon is characteristic of focal baldness - the emergence of individual areas of baldness, having a round shape.
The course of this type of alopecia in most cases is benign, that is, after 4-6 months, the bald areas gradually become overgrown with hair.
So, the regression stage can be characterized by the following steps:
- In place of bald patches colorless thin hair appears, in the form of a gun.
- Over time, the down thickens, acquires a darker color and turns into full-fledged hair.
Usually, hair growth at the regression stage occurs unevenly, that is, at the beginning you can observe active hair growth on old bald spots, while in other areas the fluff remains. However, after the time has elapsed, all the areas affected by alopecia overgrow, and a complete cure occurs.
Thus, the disease cannot be started and it is necessary to take measures on time to eliminate the first symptoms of alopecia. It should be understood that in most cases, the susceptibility to hair loss is transmitted at the genetic level, so in this case the treatment is meaningless.
Diffuse baldness
If we consider all types of baldness in men, the next most common is considered to be an irredurant alopecia, which can be triggered by the aggressive effects of external factors. A distinctive feature of this type of hair problem is uniform hair loss over the entire head. Today in medical practice, two forms of diffuse alopecia are considered - telogen and anagen form.
Telogen form
If adverse factors act on the scalp and hair roots, the hair follicles go into a state of rest, which is called the telogen phase in medicine. In general, in terms of the norm, about 15% of the scalp should be in the telogen stage, but with a diagnosis of diffuse telogen alopecia, doctors diagnose up to 80% of hair in the long-term rest.

The causes of telogen diffuse alopecia may be as follows:
- nerve loads, stress, mental stress in a chronic form,
- low protein diets
- vitamin deficiency
- acute, chronic, somatic, systemic and infectious diseases,
- long-term use of antibiotics, antidepressants, antipsychotics, antitumor drugs, etc.,
- hormonal disorders and thyroid disease.
Anagen form
If we consider the anagen form of diffuse alopecia, doctors talk about the pronounced damaging effect of aggressive factors on the hair, with the result that they simply do not have time to go into the rest phase, falling on the anagen growth phase. In this case, there is a long period between the aggressive effects of factors and the onset of hair loss.
The causes of the anagen form are as follows:
- unfavorable ecological situation
- intoxication of the body,
- radiation, chemotherapy,
- radiation effect
- treatment with toxic chemotherapeutic drugs.
Treatment of diffuse hair loss
Despite the advertising of various means and procedures, trichologists insist that diffuse alopecia and even its initial degrees are not treated as such. The fact is, despite the negative incidents with the hair, the measles themselves and the hair follicles function as before. And there are no points on which it will be necessary to influence drugs and procedures.
The main goal of the treatment of diffuse alopecia is to identify the cause of hair problems and eliminate the provoking factors. After that, a man can speed up hair restoration at home with the help of folk remedies. Also, the doctor may prescribe pharmaceutical lotions, solutions, shampoos and balm to stimulate hair growth, strengthening the roots and hair structure. The best growth stimulants are tricomine and foligen in the form of spray, shampoo and conditioner.
Focal (Breeding) Alopecia
Focal baldness is a less common type of male alopecia, which occurs in only 5% of cases of skin diseases. Determine it can be on the basis of how balding nesting form begins. First, there is a gradual thinning of the hair in one or several areas of the head, after which you can see rounded even areas of bald spots in the back of the head.
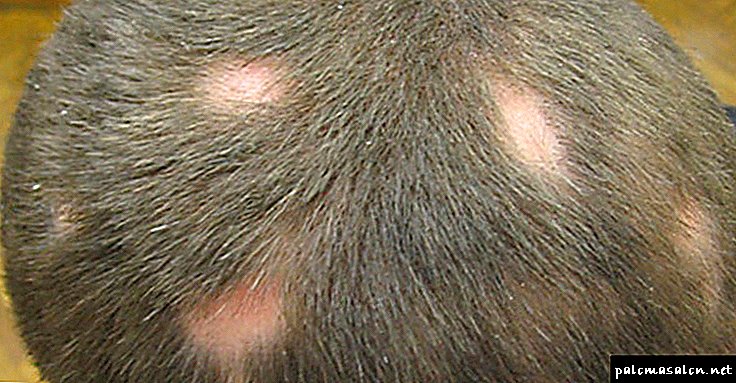
Causes of disease
The etiology of focal alopecia is still under study by specialists, doctors note the following possible factors:
- heredity,
- hypo-, hyper- or avitaminosis,
- increased production of dihydrotestosterone,
- chronic infections and viral diseases,
- diseases of the digestive system,
- defects of follicles of congenital nature,
- prolonged contact with chemical and toxic substances, radiation and radiation,
- impaired metabolism
- overload of psycho-emotional background, stress, depression,
- chemotherapy,
- taking potent drugs such as neuroleptics, anti-inflammatory and anticancer drugs, antibiotics, antidepressants, etc.,
- bad habits and poor nutrition, lack of exercise,
- autoimmune processes in the body.
Stages of alopecia areata
The symptoms and clinical manifestations will help determine the stage of development of alopecia areata, as well as the doctor trichologist, who knows for sure how to determine the phase of the disease. Stages of alopecia may be as follows:
- active phase - the patient may experience swelling and redness, itching and a burning sensation in the area of hair loss, and the hairs themselves are easily separated from the skin when in contact with them,
- stationary phase - in the area of hair loss there is a pale spot without hair, normal hair roots and follicles are visible on the border,
- remission phase - in place of bald patches, the appearance of downy hair is visible, but with insufficient pigmentation.

In addition to changes in the condition of the hair, doctors often diagnose changes in the nail plate, namely, a rough surface, deep grooves, white blotches, nail lamination and brittleness. If the doctor is watching the total distribution of alopecia areata, in 95% of cases there will be problems with the nails.
Treatment of focal baldness
Regardless of which stages of alopecia alopecia are observed in a patient, therapeutic measures will be complex and phased. First, the causes of alopecia are determined, in connection with which corrective treatment is prescribed. It may be as follows:
- the use of hormonal drugs prednisone or glucocorticoids,
- treatment to restore the balance of sex hormones,
- local treatment to restore hair by reviving the follicles, stimulating growth,
- the use of folk remedies to stimulate hair growth (masks with mustard and red pepper, oil masks and herbal rinses),
- correction of immunity,
- physiotherapy methods to increase the effectiveness of therapy, for example, darsonvalization, current stimulation, mesotherapy, massage, etc.,
- correction of diet and lifestyle.

Particular attention should be paid to the man the choice of cosmetics. The trichologist may prescribe shampoos, balms, lotions and solutions for the topical treatment of hair containing components that accelerate blood flow. Due to this effect, the nutrition of the hair roots is getting better, and dormant follicles awaken.
Cicatricial Alopecia
Cicatricial alopecia is accompanied by massive hair loss due to the formation of scarred atrophic lesions on the scalp. That is, in simple terms, it will be traumatic alopecia, triggered by external and internal factors. The formation of scars can be caused by wounds and cuts, and may be the result of inflammatory or infectious diseases that affect the hair follicles, leaving after compaction.
Causes of cicatricial alopecia may be as follows:
- acquired or congenital developmental abnormalities of the hair follicles,
- severe infections, such as syphilis, leishmaniasis, leprosy, etc.,
- oncologic neoplasms,
- physical provocateurs, such as exposure to temperature, radiation, acids, mechanical injuries,
- systemic diseases, whether it is sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, etc.,
- flat red lichen.

If a man has a first degree of alopecia of cicatricial appearance, the outlined areas of small size baldness may be slightly visible on the scalp. If visible and enlarged foci are seen, it may be alopecia of 2 degrees. The patient will feel discomfort, burning and itching in these areas, against the background of which inflammatory reactions, pus, dryness and peeling of the skin can occur. Then all the signs and symptoms disappear, leaving the bald patches.
Doctors emphasize that cicatricial alopecia is the most serious problem of hair, which is rarely amenable to conservative treatment. Only by accurately determining the causes of alopecia at the initial stage of its development, can the pathological process be stopped. Otherwise, it will be possible to restore the previous hair growth only surgically - hair transplantation from the donor site. But even here the forecasts will be very ambiguous, whether the tissue on the scar skin will take root is unknown.
Only by knowing the first signs of alopecia can a man be able to see a doctor in time to prevent the pathological process. Only knowing the causes of hair loss, the trichologist will be able to choose an effective treatment course, restoring the patient's hair health. Today, the most common androgenic and diffuse forms of alopecia, cicatricial and focal baldness are more difficult to treat.
Why does alopecia occur?
The issue of male pattern baldness is today the most pressing one and is the No. 1 problem. Speaking about male pattern baldness, several important factors should be taken into account that have a direct and significant effect on this process. These factors are due to:
- genetic inheritance
- certain hormones
- by age.
The first factor - genetic inheritance occurs in the practice of medicine quite often and affects most of the stronger sex. In the case of genetics, the disease is difficult to treat and can affect a person at an early age, closer to 20 years. Baldness is hereditary, stably moving from one generation to another.
The hormonal factor is caused by the predominance of the hormone dihydrotestosterone in the body of men, which has a detrimental and destructive effect on the hair follicles, preventing normal hair growth. In some cases, there is an inadequate response of the hair follicles to dihydrotestosterone, as a result of which the nourishment of the hair stops, they become weak, thin and colorless over time.
The treatment gives a positive result if the patient organizes a timely visit to the doctor at the very beginning of the development of the disease, when the process of prolapse affects only the frontal part. The treatment is aimed at bringing the dihydrotestosterone level back to normal with parallel use of other medical procedures.
And finally, the last factor - age. Unfortunately, with age almost 95% of men undergo the balding process as a result of the simultaneous influence of several factors, as well as the inability of some hair follicles to perform their functions, in particular, feeding the hair and stimulating their growth. Therefore, over the years, the hair in the frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital parts begin to thin out or finally fall out, increasing the area of baldness.
Hamilton-Norwood Baldness Classification
According to the existing classification, there are 7 degrees of male pattern baldness:
- The first degree (stage 1) is characterized by a minimal groove (hair loss) along the front line of hair, mainly in the areas of the forehead and temple,
- The second degree (stage 2) is characterized by the fact that hair loss along their anterior line, again in the frontal and temporal regions, takes a triangular shape. The recess zone can have both symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes. Deepening (baldness) covers an area of not more than 2 cm from the front line of hair growth. The hair either falls out completely or becomes sparse on the parietal region, but differs in density from the frontal and temporal regions,
- The third degree (stage 3) is due to the greatest degree of hair loss in the area of alopecia under consideration. There are deep frontal and temporal bald patches, usually symmetrical, sparsely covered with hair. At this stage, the bald areas extend from the hairline further than 2 cm,
- The third degree (stage 3A - crown) is characterized by hair loss mainly at the crown. There may be a slight frontal alopecia, but it almost does not exceed the area of hair loss, which was considered at the previous stage. Usually, crown hair loss is associated with age, but it is possible that the beginning of the process can be observed at an early age.
- The fourth degree (stage 4) is due to pronounced frontal and frontal-temporal alopecia than in the previous stages. In the area of the top of the hair exposed to partial or complete loss. And although the frontal and crown regions are extensive, they are separated from each other by hair, which completely connects the rim of hair on both sides of the head,
- The fifth degree (stage 5) is determined by the fact that the crown region of hair loss is separated from the fronto-temporal region. The hair between them, forming a narrow band, becomes sparse. The balding process covers a large area, as a result of which a horseshoe-shaped hair is formed and observed,
- The sixth degree (stage 6) is characterized by the fact that the strip of hair that still separated the frontal and top areas is now lost. Therefore, the fronto-temporal and crown regions merge to form one common and larger bald spot,
- The seventh degree (stage 7) is the most serious form of male pattern baldness. There is complete baldness in the area, starting with the forehead and ending with the nape. Hair remains only on the lateral surfaces of the head (ear area) and extend back, dropping below the neck.

In the case of women, the balding process has a slightly different picture. Unlike men, baldness begins closer to 30 years and lasts up to 50 years. Hair loss is diffuse and lasts much longer. Full alopecia does not occur, but the hair in the area under consideration noticeably thin. As in men, the region of prolapse is the frontal, temporal, and occipital parts.
The main causes of alopecia in women in this case are:
- hormonal changes, that is, with the direct use of contraceptives by women,
- the postpartum period, when there is a marked weakening of the immune system,
- menopausal or post-menopausal periods.
These causes of baldness are observed in women at the age of 30 to 50 years.
How to replant hair
It is believed that when androgenetic alopecia hair loss in men and women differs in clinical manifestations, therefore, classification is used to determine the degree of male pattern baldness Norwoodand classification Ludwig to determine the extent of hair loss in women.
Complete non-surgical hair transplant HFE is suitable for everyone, as it allows:
1. Conduct both small and super small hair transplants (grade 1, small foci, scars), and the largest (grade 4, 5, 6, 7 according to Norwood) - in just a few hours,
2. Protect your head and scalp from scars and scars, as well as postoperative swelling and numbness of the scalp and many months of headaches,
3. Break the transplant into 2 or even 3 procedures, since there are no cuts or scars, which is especially convenient if you:
- you can not stand many hours of intervention in the vital activity of the organism,
- unable to financially pay immediately the cost of a big hair transplant.
4. Simulate the design of your future hairstyle up to every hair,
5. To achieve the actual natural density - up to 75-80 hairs per 1 cm 2,
6. Save each of your native hairs, since microtools are very thin and are able to replant closely transplants to native hair without damaging them,
7. Save your time, because after the procedure you:
- no longer tied to the clinic (dressing changes, medical treatment of the head and medical observation are not required, and so on),
- keep your appearance natural, as you do not have post-traumatic swelling, bruises, headaches and a long scar on your head after transplantation,
- lead a normal rhythm of life and do not lose the ability to work.
8. The donor area is not damaged (not cut) and, if necessary (if your native hair continues to fall out), the procedure can be performed repeatedly,
9. Save your emotional state and sense of usefulness (by the way, after the operation, the scar not only heals for 3-6 months, but remains on the head for life, and after the procedure Hfe microranks heal in 3-5 days, leaving no visible damage).
Degree of hair loss in men
Today, Norwood's classification includes 7 degrees of male androgenetic alopecia with several subtypes. Degree 0 (Fig. 0) is not included in the classification, but we will use it as a reference - for a complete picture of what a man should look like, whose hair is not susceptible to androgenetic alopecia.
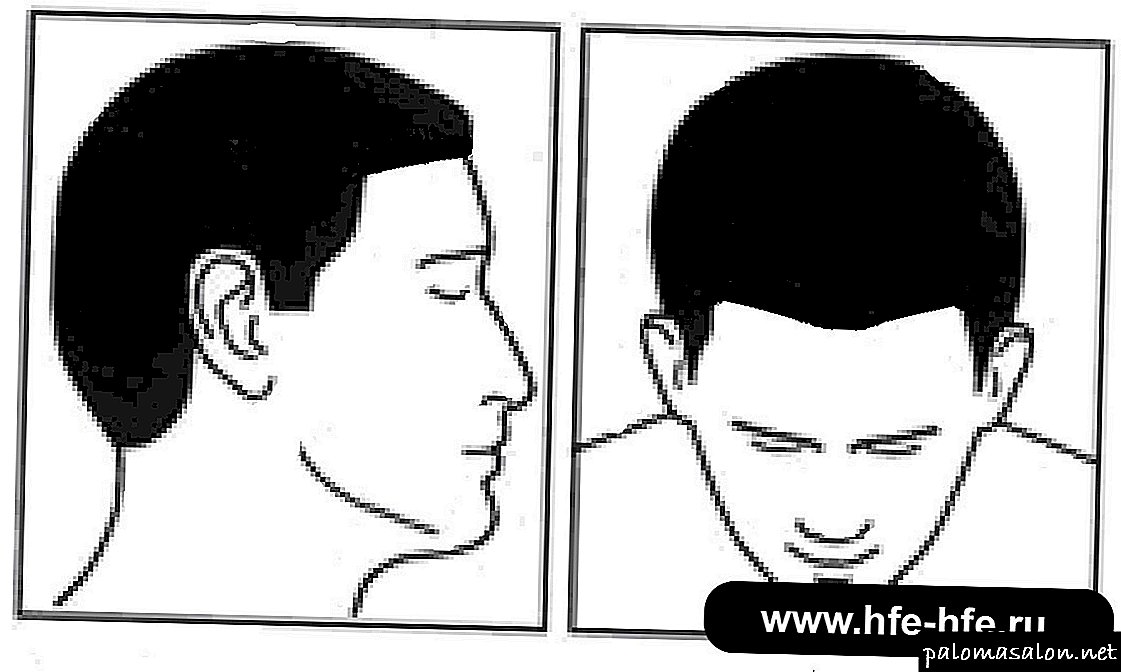

Fig. 0
Choose your type (degree) of hair loss in order to familiarize yourself with the features of hair loss and their restoration with the non-invasive HFE technique.
Androgen-genetic alopecia (AHA):
The most popular and generally accepted classification of androgenic hair loss according to the female type is the Ludwig system proposed in 1977.
This type of hair loss is likely to occur during hormonal changes, that is: when using improperly chosen contraceptives, after childbirth, during menopause and / or after it.
Androgenetic hair loss according to the female type is characterized by the presence of a center of thinning hair in the central parietal region, which has oval outlines. A characteristic feature is the absence of baldness on the temples and above the forehead. Hair loss occurs diffusely and becomes noticeable later than in men, most often between the ages of 30 to 50 years.
Cicatricial and traction alopecia:
The second most common reason for hair transplantation in women is scar and traction alopecia.The most common causes include traction alopecia (tightly tightened hair, African pigtails, wearing “extensions” or false hair, etc.) and scars after neurosurgical and plastic surgeries (circular face lift, etc.).
You can read more about cicatricial alopecia in the “Alopecia” section.
HFE non-surgical hair transplant technique allows you to completely close the hair loss sites, as well as transplant hair into the area of existing scars. It should be understood that the survival of hair in the scar tissue is somewhat reduced compared with intact scalp and is not more than 65-70%.
According to the classification of Ludwig, there are 3 degrees of hair loss.

Grade 1. The majority of women prone to baldness refers to the first gradation of the Ludwig system. Usually this stage of hair loss is typical for women 20-35 years of age. There are cases when hair loss begins at the age of 17-18. At the initial stages, thinning of the hair can affect either the frontal-central part of the head more, not reaching the top of the head, or, conversely, only the parietal zone, without touching the central part of the head. With this type of alopecia, it is usually indicated to transplant 700-1100 FU. With a pronounced first degree, gaps are observed throughout the central parietal zone. Among the completely healthy hair there are weakened and even thinned hair. When the first degree of hair loss requires a transplant of 1.2-1.5 thousand follicular associations.
Grade 2. If the number of gaps on the head increases, then the second stage of female alopecia begins. Hair loss is especially noticeable if a woman wears her hair on a parted or smooth hair, such as a horse's tail. The second degree of alopecia is characterized not only by an increase in the number of lumens in the central parietal region, but also by a large number of thinned hair. The second stage is characteristic mainly of women aged 35 and older. In order to eliminate the consequences of alopecia of the second gradation, 1.7-2.5 thousand FU are required.
Grade 3. The third degree of hair loss is an extremely rare variant of female alopecia, when it is shown to transplant 3.0 thousand FU and more. Thinning takes up the entire central parietal zone, and the remaining hair is so thin that it is virtually invisible and more closely resembles gun hair. At the third stage of thinning, the first hairline also changes: in the center it is, in fact, absent.
Pre-procedure preparation for hair transplantation, microsurgical instruments, local anesthesia, the method of obtaining grafts, implantation of the hair received and its engraftment, in men and women do not differ. However, it should be noted that women sometimes have a later onset of hair growth (3-4 months) after transplantation. This is due to the physiological characteristics of the female body.
FAQ dropout
men's hair
I do weightlifting and now is pre-competitive preparation. It will go about 2 months, so I would not want to postpone this issue for a long time. How long will I need after the operation, and in general will I need to take a break in sports?
Good afternoon, tell me, after hair transplantation, you can continue to use Minoxidil, to massage the head to preserve your hair. And how it will affect the transplanted hair.
Patient Reviews
Hfe
Yura, August 8, 2018 Good day! Thought about what to visit you.
Ilya. Krasnodar, July 13, 2018 I want to once again express my gratitude to all the staff of the clinic! Special thanks to the doctor Oksana Nikolaevna! She made me a transplant 3 times.

Commercial Director of the clinic
HFE, leading trichologist