Inflammation of the hair follicle is called folliculitis. This is a disease that occurs in the follicle due to the fault of fungal, bacterial, viral and other pathogens. The cause of the onset of the disease may be a weakening of the immune system on the background of hypothermia or illness
The cause of the onset of the disease may be a weakening of the immune system on the background of hypothermia or illness
Focal infection of the contents of the hair bag, which can affect only the upper part of the follicle, or extend to its root, sebaceous and sweat glands.
At the same time on the surface of the skin appears first redness around the hair, and then a bubble with pus. In some cases, this phenomenon is solitary, in others a person has a lot of ulcers, and you can talk about a rash.
The spread of the disease, symptoms
Most often, the disease is found in countries with a warm and humid climate. In these conditions, infectious agents multiply actively, so folliculitis has become a common ailment. It refers to pyodermatitis.

The folliculitis of the hairy part of the scalp is especially dangerous, since it is in this area that the hair bag is very deep. Aggravated, infection can lead to various complications.
Symptoms of folliculitis include:
- local redness around the base of the hair,
- the formation of purulent pustules,
- on the place of the broken pustules there are sores, which then become covered with a crust,
- after complete healing, a scar or pigment can remain on the skin,
- itching, pain in the area of inflammation in the first two stages.
If the disease appears to be a rash, many follicles are affected on the body, then the patient has all of these symptoms. Some foci are just appearing, some have already festering and burst, from old ulcers there are scars, white scars or dark pigmented spots.

Causes of folliculitis and its types
The process proceeds as follows: the infection enters the hair bag and develops, causing inflammation of the hair follicles. However, the reasons why it is activated, a lot. First of all, it is untimely and improper hygienic skin care.

Indirectly affect the fall in the level of local immunity can:
- Diabetes.
- Unbalanced nutrition.
- A number of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Some diseases of the endocrine system.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Liver disease.
- Use of corticosteroids and antibiotics.
- Supercooling of the body.
- Microtrauma of the skin.
Classification of folliculitis is carried out on the basis of which pathogens provoked inflammation of the hair follicle. In this case, it is often possible to determine the type of the disease only after testing.
Bacterial
This is the most common type of disease, which in turn, in 90% of cases, is caused by golden or white staphylococcus. Pseudomonadal folliculitis and inflammation caused by gram-negative bacteria.
Mushrooms of the genus Candida and dermatophytes often affect the follicles of the scalp, beard and mustache, that is, areas with deep hair bags. There are several other varieties of fungi that can cause disease.

Most commonly caused by the herpes virus. It occurs in patients infected with this common pathogen.
Possible complications of the disease
Complications of this common disease occur when the patient is not engaged in treatment and does not follow hygiene. At the same time, neglected inflammations leave behind white scars, which are absorbed for a long time.
Unnoticed often remains inflammation of the hair follicles on the head, which can become deep and extensive.

The most common complication is a boil, which can occur at the site of an inflamed bulb. In the thicker skin appears inflammation 2-3 cm thick, which is characterized by density and soreness.
Then a necrotic rod appears in the form of a purulent vesicle, sometimes quite large. In humans, the temperature may rise, there are signs of intoxication.
A boil can develop into an abscess, which is characterized by a large amount of accumulated pus. It can also form carbuncle - several boils, which are formed on the surface areas of necrosis, black dead skin.

If the causative agent is a fungus, a large area may be formed that is affected by dermatophytosis.
There are cases when folliculitis provoked deadly diseases such as meningitis, pneumonia and nephritis. But such phenomena are extremely rare, and usually arise on the background of a serious immunodeficiency.
Diagnosis of folliculitis
When referring to a doctor, a patient is examined, as the disease has pronounced symptoms. For folliculitis characteristic:
- at the roots of the hair pustules are found with pus,
- there is a slight redness around each inflammation,
- the rash is chaotic, has accumulations.
Asking clarifying questions about comorbidities, the time of the first rash and other symptoms, the specialist can often make a fairly reliable guess about what caused the disease.

To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory tests are conducted:
- A smear is taken for Gram stain.
- A blood test from a vein to liver enzymes, from a finger to the level of sugar content.
- Bacterial seeding of the contents of purulent sacs is done.
- In rare cases, a skin biopsy is required.
At the same time, the doctor must reliably determine that he is dealing with this particular disease, and not with a similar one.
Symptoms of folliculitis can also cause such phenomena as pink or common acne, lichen redness, Kirle's disease, follicular keratosis or toxidermia. Sometimes the inflammation of the follicle generally has a non-infectious nature, for example, due to an allergic reaction.
Treatment of follicle inflammation
In the case when most of the rash is superficial, there are no foci of deep inflammation, ointments and compresses are prescribed as a treatment.
Effective means with salicylic acid, as well as salicylic and camphor alcohol. Treatment with antiseptics is also required in cases where deep suppurations are detected. They are opened and washed.

Independent autopsy of pustules and papules is unacceptable! Illiterate intervention can provoke a worsening of the situation, the spread of infection in the tissues adjacent to the hair bag. In addition, most often it leads to the appearance of scars at the site of the inflamed follicle.
Depending on the cause of the disease, antibiotics or immunostimulants, antifungal drugs may be required. It is possible to supplement the treatment of folliculitis with physiotherapy, laser correction. Effectively UV exposure.
Simple treatment is quite effective, although the patient is required to comply with all the recommendations of the doctor:
- do not take hot baths, do not swim in public reservoirs, baths and saunas,
- do not squeeze purulent discharge, monitor hygiene,
- Do not wear hot or irritating skin.
Apply and traditional methods of treatment, which are based on the anti-inflammatory effect of herbal preparations and the elimination of vitamin-mineral imbalance.

They are used in addition to medical recommendations.
Disease prevention
If you have a tendency to folliculitis, you must follow the rules of personal hygiene: regularly change clothes, wash your hair and take a shower, after epilating or shaving, wipe your skin with salicylic acid preparations.

It is also important to wear comfortable clothes from natural fabrics, use high-quality skin and hair care products, and cosmetics.
 Good effect gives external application of chamomile decoction, as this plant perfectly reduces inflammation.
Good effect gives external application of chamomile decoction, as this plant perfectly reduces inflammation.
A significant role in prevention is played by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, a full and varied diet.
When symptoms appear, you should consult a dermatologist, as it is possible to treat folliculitis only when the cause of inflammation is correctly established.
Self-treatment can lead to the transition of the disease to a chronic condition.
What is a hair follicle
The hair follicle is the pore that is the receptacle of the hair root, where the hair shaft is formed and from there grows out.

It depends on him what will be the structure, color and length of the hair. The hair follicle is located in the dermal layer. Consists of the following parts:
- hair bulb,
- follicular funnel,
- root vagina,
- retention muscle.
It also communicates with capillaries, sweat and sebaceous glands. The capillaries are responsible for nutrition, and the sebaceous glands for lubricating the hair with the sebaceous secret, which protects against aggressive environmental influences. But in the absence of proper hygiene or an excess of sebum production, it is the activity of the sebaceous gland that contributes most to the inflammatory process.
The close proximity of the hair follicles to the surface makes them a target for infections and various fungi, especially if they are damaged during the epilation process. Another common cause of inflammation is blockage of the excretory duct of a hair bag with dirt, particles of dead skin, or hardened sebaceous secretions. In this case, sweat with a greasy secret cannot find a way out, accumulating in the hair follicle. And as you know, sebum and sweat are a good breeding ground for bacteria, fungi and viruses.

The inflammatory process in the hair follicle is called folliculitis. It is one of the varieties of pyoderma - purulent diseases of the skin layer caused by the activity of microorganisms.
If only one follicle is inflamed, then we are most likely talking about non-compliance with hygiene, but in the case when there are several, you can already classify them as a rash. This means that it is not only a matter of non-compliance with hygiene. The causes of inflammation of the hair follicle may be as follows:
- allergic reaction,
- reduced immunity
- colds,
- hormonal disruptions
- fungal infection
- diabetes,
- avitaminosis,
- violation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Such sexually transmitted diseases as gonorrhea, syphilis are also accompanied by folliculitis.
The disease proceeds in several stages:
- Inflammation of the hair bag, slight redness around the hair.
- Inflammation of the hair bag down to the root, forms a pustule that begins to fill with pus.
- Inflammation affects the entire follicle and the sweat and sebaceous glands that communicate with it, with the naked eye a noticeably large amount of pus in the pustules.
- A simple folliculitis is completed either by the fact that the inflammation is fading away, or by an autopsy.
- In the event of an unfavorable outcome, it develops into a complicated folliculitis.
But you should not count on the fact that the abscess will open itself and everything will pass. If you do not do it in time and in sterile conditions, then the folliculitis can be burdened by complications, scars will remain.
Folliculitis is classified according to several criteria. By severity divided into the following:
If this is a light or medium appearance, then after opening the pustules, the disease will decline.
According to the type of microorganisms that caused inflammation, folliculitis is divided into the following types:
- bacterial,
- infectious,
- pseudomonad,
- parasitic,
- fungal,
- viral.
According to the localization on the body:
- genitals,
- scalp,
- cheeks and chin in men
- eyelashes,
- armpits,
- the rest of the body.
According to the degree of damage can be superficial (no more than 5-7 mm) and deep (10 mm). It can be deep in the case of a superficial complication, or it can be so initially if it is caused by a secondary infection. In this case, a painful nodule first appears from the outside. After about 5 days, the abscess itself is shown in place of the nodule.
By the nature of the flow can be acute and chronic. Untreated acute can develop into chronic. When inflammation affects adjacent follicles again and again. And in the same follicle from time to time, the inflammation can subside and flare up.
Folliculitis caused by careless shaving and disregarding disinfection after it is called sycosis.
This is essentially the same folliculitis, but more specific localization. Ophthalmologists call it hordeolum. This purulent inflammation of the hair sac eyelashes. Accompanied by redness of the eyelid skin and the formation of pustules with pus. A rather painful formation due to the location, it is often impossible to even open the eye due to swelling and pus.
The main cause is the ingress of Staphylococcus aureus into the hair follicle with reduced immunity.
It is necessary to apply urgently - and not to a dermatologist, but to an ophthalmologist. If an autopsy is shown, it is performed exclusively in the hospital. How to treat inflammation of the hair follicle on the eye at home? Such an idea in serious cases is extremely unreasonable and is fraught with even loss of vision.
Inflammation of the head
As in the case of barley, the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus is considered to be the main cause of inflammation of the hair follicle on the head. But its carrier is about 20% of the total population of the globe, and not all of them suffer from folliculitis. Because something should provoke folliculitis. This is usually a decrease in immunity or neglect of hygiene. Folliculitis of the scalp, caused by staphylococcus, called ostiofollikulit.

But it can also occur in older people suffering from cerebral arteriosclerosis. They are tormented by the unbearable itching of the hairy part of the scalp, and they infect the hair follicles damaged by combing.
In men, it is found on the head that undermines Hoffmann's folliculitis. It is characterized by hair loss on the affected part and the separation of pus from an open fistula.
The inflammation of the hair follicle on the head is particularly unpleasant in that it is accompanied by partial alopecia. The affected area is difficult to treat with local ointments, if you do not shave your hair. And for many it is quite tragic. In especially neglected cases, the folliculitis leaves scars behind it, in place of which the hair will never grow. Therefore, it is better to treat it completely, not leading to complications.
Ingrown hair
Due to frequent epilation and poor-quality exfoliation of the body in front of her hair, there can be no way out because of the overgrowth of the hair follicle. In this case, it changes its direction and begins to grow inward. Like any foreign body, it causes inflammation. If the hair has not grown far, and the folliculitis has not grown into a severe stage, it is sometimes sufficient to simply conduct a high-quality exfoliation of the body. Then the hair will be available so that it can be picked up with tweezers and pulled to the surface. It is advisable to carry out this procedure with a beautician and be sure to under sterile conditions. Since it will no longer grow in this case, the inflammation should also disappear. If the folliculitis managed to develop quite strongly, then you still need to contact a dermatologist.He will open the inflamed follicle, drain the cavity and prescribe a standard treatment for such a case.
The most prominent of the symptoms of inflammation of the hair follicle is the formation of a bubble of pus around the hair. The area around it will be painful, especially when pressed, prone to hyperemia. But other symptoms of different types of folliculitis may vary.
Bacterial often affects those places that are exposed to razors or friction. It has a multiple character and is accompanied by intolerable itching.
Infectious may be accompanied by alopecia, it is difficult to external treatment, as the problem is inside the body.
Hofmann folliculitis forms a rounded area that changes its color to jaundice blue with fluctuating contents inside. It stops growing hair, and when pressed, pus is released.
Pseudomonad is characterized by the fact that the symptoms appear after taking water procedures, including at home. The main reason is infection with a pyocyanic stick in ponds and pools. The very contact with Pseudomonas aeruginosa will not necessarily entail pseudomonadal folliculitis. But after bathing in public places it is better to wash the body with antibacterial soap. Most common in children.
Complications
In most cases, folliculitis does not pose a serious hazard. But if the disease is neglected, the root cause is not eliminated, or the immune system is weakened, serious complications can appear, such as abscess, furuncle, scars, carbuncle and alopecia of the scalp.
An abscess is an inflammation on the deep layers of the dermis that does not have pus out. Gradual replacement of normal tissues with purulent cavities occurs. It has quite serious consequences and requires urgent opening and drainage of the cavity.
Carbuncle is an inflammation of the hair follicles, but in an acute form, accompanied by partial necrosis of the affected tissues. When carbuncle inflammation goes to the deepest layers of the dermis. The spectacle is not for the faint hearted and threatens with inflammation of the soft tissues located under the dermis. Accompanied by intoxication of the body. From the Latin carbunculus translates as "ember". This name was received because of its external resemblance to a burn.
Furunculosis or the formation of chirya is also a complication of folliculitis. This is an inflammatory process that spread from the follicle to the connective tissue and is accompanied by necrotic lesions. It is very difficult to cure it to the end, and it constantly appears again and again, in especially severe cases it does not pass at all. Launched furunculosis can damage the rhizome of the hair irrevocably. And this means that even after the furuncle passes, the hair in this place will never grow. And also a rather serious scar can remain. These complications are purely cosmetic and do not carry a health hazard.
What is folliculitis
Folliculitis - Infectious lesion of the middle and deep sections of the hair follicle, leading to its purulent inflammation. Folliculitis can have a bacterial, fungal, viral, parasitic etiology. It is manifested by the appearance in the places of hair growth of single or multiple pustules, in the center of which the hair passes. Opened pustules form ulcers, their healing with a deep lesion of the hair follicle is accompanied by scarring. Diagnosis of folliculitis is carried out by dermatoscopy, smear microscopy and examination of detachable pustules. Treatment is carried out with solutions of aniline dyes, antiseptics, local and systemic use of etiotropic drugs: antibiotics, antimycotics, acyclovir.
Along with hydradenitis, sycosis, streptoderma and streptococcal impetigo-folliculitis refers to purulent skin diseases (pyoderma), whose prevalence among the population reaches 40%.
In hot countries, the incidence of folliculitis is higher because the climate itself contributes to the development of infection. A high incidence rate is also noted among socially disadvantaged segments of the population living in unsanitary conditions.
In some cases, folliculitis begins with ostiofollikulit - superficial inflammation of the hair follicle, exciting only his mouth. Further spread of the infection to the depth of the follicle leads to the transformation of the ostiofolliculitis into the folliculitis.
Epidemiology. Statistical data
Folliculitis is most common in hot countries where the climate favors the development of inflammatory skin diseases. Also, this disease is more common in socially unfavorable strata of society, which is facilitated by unsanitary conditions of life.
Accurate statistics are not provided, since in most cases such patients rarely seek medical help, preferring to self-medicate. In the field of view of physicians are most often patients who have developed complications against the background of folliculitis: phlegmon, abscess or lymphadenitis.
Folliculitis symptoms
Folliculitis begins with redness and infiltration in the area of the hair follicle. Then a conical pustule penetrated with downy hair is formed with purulent contents in the center. After its opening and release from pus, a small ulcer is formed, covered with a bloody-purulent crust. If the entire follicle is affected, hyperpigmentation or a scar remains on the skin after the skin is peeled. More superficial folliculitis may resolve, leaving no trace behind. The process of development and resolution of inflammation of one follicle takes up to 1 week.
Most often the folliculitis is multiple in nature. Its elements are usually located on the hairy areas of the skin: on the face, head, in the armpits, in the groin, on the legs (mainly in women depilating the legs and thighs). The rash is accompanied by pain and itching of varying severity. In the absence of correct treatment and hygienic measures, folliculitis is complicated by the development of boils, carbuncles, hydradenitis, abscesses, and phlegmon.
Staphylococcal folliculitis usually localized in areas of bristly hair growth, most often it is the chin and skin around the mouth. It is found mainly in men who shave their beards and mustaches. May be complicated by the development of sycosis.
Pseudomonas folliculitis It is popularly called “hot folliculitis”, because in most cases it occurs after taking a hot bath with insufficient chlorination of water. Often develops in patients undergoing antibiotic treatment for acne. Clinically expressed in a sharp increase in acne, the appearance on the face and upper body pierced with hair pustules.
Syphilitic folliculitis (acne syphilis) develops in secondary syphilis, accompanied by non-scar alopecia in the growth zone of the beard and mustache, as well as the scalp.
Gonorrheal folliculitis is a complication of untreated and long-lasting gonorrhea. Favorite localization - the skin of the perineum in women and the foreskin in men.
Candida folliculitis observed mainly with occlusive dressings, in bedridden patients and with prolonged fever.
Dermatophytic folliculitis characterized by the onset of inflammatory changes from the superficial horny layer of the epidermis. The process then gradually captures the follicle and hair shaft. May occur on the background of trichophytia and favus, leaving cicatricial changes.
Herpetic folliculitis characterized by the formation of vesicles in the mouths of the hair follicles. Observed on the skin of the chin and nasolabial triangle, often in men.
Folliculitis, caused by demodicosis, is manifested by reddening of the skin with the formation of characteristic pustules in the mouths of hair follicles, around which a scaly peeling is noted.
Impetigo Bockhart - Another version of folliculitis. It develops with skin maceration. Most often occurs with hyperhidrosis or as a result of therapy with warming compresses.
Folliculitis Treatment
Folliculitis therapy should be consistent with its etiology. With the bacterial genesis of folliculitis, ointments with antibiotics are prescribed, with fungal - antifungal drugs, treatment of herpetic folliculitis is carried out with acyclovir.
At the beginning of the disease, local treatment and treatment of lesions with solutions of aniline dyes (fukartsin, brilliant green, methylene blue) are sufficient. To prevent the spread of infection to healthy areas of the skin, they are treated with salicylic or boric alcohol. Additionally applied UFO.
Cases of severe recurrent folliculitis require systemic therapy. For staphylococcal folliculitis, cephalexin, dicloxacillin, erythromycin are prescribed inside. Treatment of severe forms of pseudomonad folliculitis is performed with ciprofloxacin. For candidal folliculitis, fluconazole and itraconazole are used, and for dermatophyte folliculitis, terbinafine is used. At the same time, they carry out therapy for concomitant diabetes mellitus or immunodeficiency states.
How to treat inflammation of the hair follicle
At the initial stage of the disease, treatment of pustules with suitable means is sufficient. Camphor (2%) and salicylic alcohol (1-2%), solution of brilliant green (2%) or methylene blue, fucorcin are suitable for this. Now gels, creams and lotions of the series Klerasil are very popular. If the disease affects the deeper layers of the skin and is accompanied by significant purulent accumulations, it is necessary to open the bubbles, remove their contents, and then treat with one of the listed agents. It is recommended to apply ichthyol compresses twice a day.
If the disease has become chronic and relapses, serious medical therapy is required. In this case, antibiotics and sulfonamide drugs are prescribed. Immunostimulating therapy is also indicated.
When inflammation of the hair follicles is observed on the arms, legs, torso, it is impossible to squeeze the affected parts of the body and squeeze the bubbles, as this increases the risk of developing boils and even phlegmon. Well-proven investment in ultraviolet rays. The general course is 6-10 procedures. Sessions are prescribed every day or every other day. If folliculitis has occurred on the background of diabetes mellitus, a corrective diet is prescribed in order to normalize carbohydrate metabolism and reduce the risk of disease recurrence. Treatment of staphylococcal folliculitis involves the use of ointment Muportsin or similar, an internal reception of cefalexin, dicloxacillin, erythromycin or methicillin.
In severe cases of a pseudomonadal lesion, ciprofloxacin is prescribed. If the causative agent is gram-negative bacteria, local therapy with benzoyl peroxide is necessary. In case of fungal infection, appropriate means are necessary, for internal use - terbinafine, fluconazole, intracanosol. Herpetic folliculitis should be treated with acyclovir.
Inflammation of the hair follicle in most cases has a favorable prognosis. In case of severe lesions and damage to the deeper layers of the skin, pigmentation may remain after removal of the peel. Complications of folliculitis are rare and also successfully treated with modern methods.
Alternative treatment: use of medication
Depending on the cause of the inflammation, additional measures may be recommended. If folliculitis is caused by prolonged use of hormonal drugs, they are simply canceled. Of course, this takes into account the benefits and possible risks to the patient. In addition, doctors prescribe antibacterial agents that affect the microorganism. However, before that it is necessary to pass an analysis to identify sensitivity to certain drugs. Often, doctors use the following medications: Metronidazole, Naxojin, Cefotaxime, and so on. Remember that without prior analysis, treatment may not be effective.
Ways to prevent disease
Is there any method that avoids inflammation of the hair follicle? Of course, yes. For a start, you should review your own lifestyle and observe basic hygiene.
- Regularly cleanse your body with gels and special scrubs.
- Take a shower at least once a day.
- Try not to use other people's towels, handkerchiefs and clothing.
- Avoid dubious ponds, saunas and swimming pools.
- If you are swimming, the water in an enclosed space should be chlorinated. At the same time its pH should be at least 8.
- Avoid wearing heavy underwear.
- Avoid severe friction of clothing in the area of skin folds, for example, in the groin area.
- When depilating and shaving, always use emollients. After the procedure, apply to the skin alcohol softening lotions. They will help to disinfect the integument and prevent bacteria from entering the wound.
Conclusion
It is possible to earn inflammation of the hair follicles even when testing probes in cosmetics stores. For example, mascara, which someone tested before you, can be a source of infection of the ciliary follicles. Treating them is harder and harder, so you shouldn’t put yourself at risk (learn here how to wake dormant hair follicles).
The structure of the hair and hair follicle

The hair consists of a rod, which is visible above the surface of the skin, and a root, which is located in the thickness of the skin in the hair follicle. The latter is localized in the dermis and subcutaneous adipose tissue, surrounded by a capsule of connective tissue.
At the bottom of the follicle expands. In this place is the hair follicle and papilla of connective tissue, containing nerves and blood vessels. At the top of the follicle is its mouth, into which the sebaceous and sweat (not everywhere) iron flows.
Such a complex structure contributes to the fact that inflammation can occur in different parts of it and for quite diverse reasons. Reducing the protective properties of the skin, excessive sweating, damage, scratching, ingrown hair, pollution, blockage of sebum - this is a small list of causes that can lead to an unpleasant disease.
Hair follicle occlusion and inflammation
Folliculitis refers to purulent diseases of the skin. Sometimes it is preceded by ostiofollicluitis, a superficial inflammation that affects only the mouth of the follicle.
Almost always the disease is provoked by bacteria, mainly staphylococcus. However, it can be pseudomonads, pathogens of gonorrhea, syphilis, etc. The causes can be hidden in a fungal infection (eg dermatophytes, fungi of the genus Candida), viruses (simple, herpes zoster, contagious mollusc), parasites (demodex mite). According to pathogens, inflammation is classified into bacterial, fungal, viral, syphilitic, and parasitic.

The infection penetrates through minor injuries: abrasions, scratches, excoriation, soak. People at risk of itchy dermatoses (atopic, allergic dermatitis, eczema) are at risk, as they constantly comb their skin and also suffer from hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating).
The penetration of infection contributes to the reduction of the barrier function of the skin and immunity. For example, the probability of developing the disease is higher in people with diabetes and immunodeficiency (HIV infection, immunosuppressive therapy, long-term diseases).Local immunity is reduced after prolonged use of glucocorticosteroids, as well as with regular exposure to chemicals.
Symptoms of inflammation in the hair follicle
Pathology begins with redness and infiltration, then a pustule is formed with pus, penetrated by downy hair. After opening the pustules, an ulcer is formed, covered with a purulent-bloody crust. After the discharge of the peel, scar or hyperpigmentation remains. Superficial follicles are resolved without consequences. On average, the inflammatory process lasts about a week.
As a rule, the disease is multiple, affecting the face, head, armpits, groin, legs. Rash accompanied by itching, sometimes pain.
If untreated, it arises from an inflamed follicle or furuncle or carbuncle:

- Staphylococcal inflammation - most often localized on the chin and skin around the mouth. More common in men who shave their mustache and beard. May be complicated by sycosis,
- Pseudomonas - occurs after taking a hot bath with poor chlorination of water, in patients with acne after antibiotic therapy. It is expressed by an increase in eruptions on the face, upper torso,
- Syphilitic - occurs in secondary syphilis. He is accompanied by non-scarce alopecia in the area of the beard / mustache, scalp,
- Gonorrheal disease is a consequence of the absence of gonorrhea treatment. Localized in the perineal zone in women and in the foreskin in men,
- Candida - occurs when applying occlusive dressings, with a long fever, in bedridden patients,
- Dermatophyte - is characterized by the initial inflammation of the superficial horny layer of the skin, gradually affecting the follicle and hair shaft. Often leaves scars and accompanies favus and trichophytosis,
- Herpetic - characterized by the formation of vesicles in the mouths of the follicles. Most often affects chin, nasolabial triangle,
- Caused by demodicosis - the skin turns red, pustules are surrounded by scaly peeling,
- Impetigo Bockhart - occurs during maceration. Often accompanied by hyperhidrosis and develops after the use of warming compresses.
Complication of inflammation
The furuncle appears in the absence of adequate treatment at the initial stage of inflammation. It is worth noting that the disease has a long course and is not always resolved independently, in some cases surgical intervention is necessary.

While the boil matures, it is necessary to treat the skin with antiseptics. The doctor can chop him off with antibiotic solutions and novocaine. Also prescribed with antibacterial drugs, UVA and UHF. To enhance immunity, ozone therapy, fortifying agents, autohemotransfusion, gamma globulin may be required. When a zone of fluctuation is formed, the doctor applies a special bandage to accelerate the exit of the rod.
Perhaps an independent opening of the abscess, or its surgical removal.
After that, the wound is washed with peroxide, bandaged with Vishnevsky ointment, levomekolom, sintomitsinovoy, ichthyolic or erythromycin ointment. Under local anesthesia, boils are opened during an abscess, purulent-necrotic masses are removed. The need for antibiotics occurs in chronic and multiple furunculosis, abscess, reduced immunity.
How to treat a sore hair follicle
The doctor first determines the state of the follicle and the pathogen, excludes the specific etiology of the pathology, identifies the concomitant diseases that contribute to inflammation.

Dermatoscopy allows you to determine the depth of the lesion. It is necessary to take a detachment for bacteriological seeding and microscopy, examine it for fungi and treponema pale. PCR diagnostics eliminates gonorrhea and syphilis. A blood test for sugar, an immunogram, etc. may be assigned. Differential diagnosis is also necessary.
Treatment corresponds to the etiology. In the presence of bacteria, antibacterial ointments are prescribed; in case of fungal lesions, antifungal agents, the herpetic form requires the appointment of acyclovir.
In the initial stages, local therapy is sufficient. Lesions additionally treated with aniline dyes (pr. Zelenka). To prevent the spread of infection, healthy skin is treated with boric or salicylic alcohol. UFO may be assigned.
In severe cases, systemic therapy is necessary. In the presence of staphylococci prescribe erythromycin, cephalexin, dicloxacillin inside.
Severe pseudomonad type is treated with ciprofloxacin. In candidal lesions, it requires treacinazole and fluconazole; in dermatophyte lesions, terbinafine is required.
Follicular cyst - a hair follicle malformation
In this case, there is a tumor-like benign lesion. It may be innate or it may occur much later. As a rule, the disease is inherited.
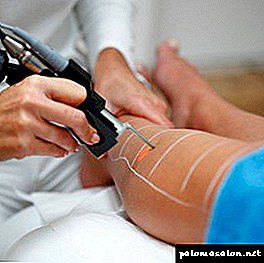
Treatment of a cyst involves its removal. If the formation is insignificant and does not cause discomfort, it does not touch, only the control in dynamics is shown. However, the removal of a cyst of the hair follicle, even of small size, is necessary in case of its inflammation.
The formation together with the capsule can be removed through an incision in the skin or by means of its exfoliation with a laser. If you do not excise all pathological tissues, a relapse of the disease will occur.
Before proceeding with the operation, you need to relieve inflammation. If the cyst is accompanied by a purulent abscess, it is necessary to open and install drainage.
In order to eliminate inflammation of the hair follicles, it is necessary to avoid injury to the head and other parts of the body, to monitor hygiene, to handle scratches and cuts with appropriate means.
What it is?
Folliculitis is an infectious disease characterized by purulent inflammation that affects the hair follicles of the middle and deep sections. The disease has a different cause: parasitic, viral, fungal and bacterial. Characteristic manifestations of folliculitis are multiple or single pustules appearing at hair growth sites through which hair passes.
Causes of development
Inflammation of the hair follicles is initiated by pathogenic microorganisms: fungi, ticks, viruses and bacteria. It becomes the residence of these organisms due to external factors or due to human health problems.
Thus, the causes of folliculitis conditionally divided into:
- exogenous (external circumstances),
- endogenous (diseases that create optimal conditions for the life of pathogenic organisms).
Among endogenous factors note:
- liver disease,
- obesity,
- low hemoglobin
- diabetes,
- malnutrition, due to which the body is deficient in certain substances.
Exogenous causes include:
- high ambient temperatures
- hypothermia,
- skin injuries (cracks or microcracks),
- incorrectly chosen clothes (made of “non-breathing” and (or) synthetic materials, cramped),
- skin contamination caused by poor hygiene or specific human work (work on the ground, activities requiring contact with certain reagents, chemicals (mechanic, auto repair employee, etc.).
Sometimes folliculitis is initiated by strange, not first glance, causes: caries, tonsillitis, gingivitis, pharyngitis, periodontal disease.
It would seem, how can a hair bulb on an arm become inflamed because of a sore mouth or throat? The point here is in the pathogens localized in the mouth, in the throat. Blood they spread throughout the body, without going through the hands. Weakened immunity is not able to put a reliable barrier around healthy organs: bacteria (viruses) reach the hair follicles and settle there.

Folliculitis symptoms
The symptoms of folliculitis will depend on what kind of folliculitis you have developed. For example, with the surface type of pustules can reach sizes up to 0.5 mm in diameter and be painless to the touch. As a rule, around them there is an inflammatory area of pink color, sometimes with a reddish tinge on the skin. Approximately on the third day, the abscesses are shrunk and covered with a brownish crust, leaving a slight peeling behind. There may also be the appearance of pigmentation on the skin.
The deep form of folliculitis is manifested by a more severe damage to the hair follicle. On the skin can appear reddish nodules up to 1 cm in diameter, which are characterized by pain. On their surface is a abscess, which is pierced with a hair. The abscess can open mainly in a few days, becomes covered with a crust, and the inflammatory nodule disappears with time.
The main complaints that a patient with folliculitis presents are soreness and itching. In some cases, there may be an enlarged lymph nodes that are located near the area of inflammation. The patient may also worry about a cosmetic defect on the skin that remains after folliculitis. This may be excessive pigmentation and scarring.
Staphylococcal folliculitis manifests itself in the initial period as a process of inflammation around the hair, starting the development of osteofolliculitis, or staphylococcal impetigo. These are small forms and sizes of pustules with dense walls that are pierced in the center by a hair. A few days later, the pustule dries out, with the formation of a cone-shaped yellow crust, which is rejected in a short time.
When conditions are not good for the patient, painful sensations arise in the affected area, which especially bother the patient with a large number of folliculitis, with pronounced infiltration. Due to the involvement in the inflammatory process of the tissue surrounding the follicle and the fusion of specific elements of the eruptions, deeper appear, with the long-term existence of a type of staphyloderma, a carbuncle, a furuncle, etc.
In the diagnosis of a disease such as folliculitis, an important role relates to the examination of the patient. The eruption of folliculitis is very characteristic and allows you to properly make a diagnosis. Additional measures of the survey will help to accurately identify the cause that could lead to the development of the disease.
Features of various types of folliculitis
There are many varieties of folliculitis, and therefore, it is advisable from a practical point of view to consider separately the features of each of them.
- Herpetic folliculitis. As well as staphylococcal, it is more common in shaving men in the area of the nasolabial triangle and on the chin.
- Tick-borne folliculitis. It develops after a tick bite, it takes longer than other varieties, it requires specific treatment of the underlying disease (if the tick is an epidemiological hazard).
- Eosinophilic folliculitis. It is observed only in an isolated group of patients (HIV-infected).
- Candida folliculitis. This type of folliculitis occurs, as a rule, under occlusive dressings. The risk of developing folliculitis increases with local use of a bandage of drugs from the group of corticosteroids. Also, the risk of disease is higher in bedridden patients and long-term febrile patients.
- Staphylococcal folliculitis. Characteristic for areas where bristly hair grows (nasolabial triangle, chin). It occurs mainly in shaving men. In severe cases, when the death of hair follicles occurs, after the end of the inflammatory process, connective tissue scars are formed.
- Acne syphilide. This type of folliculitis is due to syphilis. It is characterized by the fact that the inflamed follicles become faded red color, in some cases arranged in groups. The elimination of this pathology is possible only in the treatment of the underlying disease by specific means.
- Gram-negative folliculitis develops in immunocompromised patients who have been on antibacterial drugs for a long time due to acne. Characterized by the fact that the patient's condition deteriorates sharply, which is manifested in the strengthening of acne. The formation of abscesses is possible.
- Pseudomonadal folliculitis is caused by the pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This type of folliculitis is also known by another name - “hot bath” folliculitis, since it usually occurs after taking a bath with hot water, which has not been sufficiently chlorinated.
- Folliculitis caused by fungi belonging to the genus Pityrosporum is characteristic of a tropical and subtropical climate. It is characterized by an itchy rash of monomorphic character (papules and pustules), which is located in the mouths of the follicles. In such patients, scratches are found with localization in the shoulders, back, face and neck.
- Folliculitis caused by dermatophytes. This infection is characterized by a beginning from the upper layer of the epidermis, after which the inflammatory process captures the mouth of the follicles, and then the hair shafts. A complication in this case is dermatophytosis of the scalp.
- Gonorrheal folliculitis is most rare in comparison with other types of this disease. The place of its localization is the foreskin of men and the crotch area of women. Occurs with long-term and untreated gonorrhea. When examining the contents of the pustules in these patients revealed gonococci in large quantities.
- Professional folliculitis develops in people of certain occupations and is associated with exposure to skin irritating chemicals. In this type of disease, rashes are usually located on the back of the hands, as well as on the extensor surfaces of the forearms.
- Impetigo Bockhart (impetigo Bockhardt), despite its name, belongs, nevertheless, to the group of folliculitis. In this case, hemispherical, superficial pustules appear, which can range in size from a poppy seed to a lentil. Pustules are penetrated with downy hair, arranged in groups. The reason for the development of this folliculitis is excessive sweating and maceration of the skin, which is a consequence of the use of warming compresses.
- Depilatory folliculitis of smooth skin is another type of disease that occurs mainly in hot countries. The incidence is more susceptible to middle-aged men. Symmetry of the lesion is also characteristic of this species of folliculitis. Inflamed follicles appear evenly on the skin of the lower extremities. After the folliculitis has been removed, characteristic follicular scars remain on the skin.
How to treat folliculitis?
Single osteofolliculitis can pass on their own, without additional treatment. To avoid complications, you can use antiseptic agents for skin hygiene.
In more severe cases, use the following drugs:
- Bactericidal ointments and solutions dry the skin, relieve inflammation: Methyluracil, Betadine, Miramistin, zinc ointment. Apply 1-3 times a day
- Antibiotics locally twice a day - effects on staphylococcus (erythromycin, syntomycin ointment, Levomekol)
- Rubbing the skin with alcohol solutions (boric, salicylic, camphor alcohol, "Zelenka", methylene blue),
- Antiallergic drugs to reduce itching - Suprastin, Claritin, Lomilan,
- Pure ichthyol is applied with a thin layer on large folliculitis, an antiseptic dressing is applied on top (change once a day),
- Physiotherapy: UV, UHF, laser therapy.
Proven methods and recipes of traditional medicine:
- Compresses, soothing dressings with thistle. Boil 50 grams of root in 0.5 liters of water for half an hour. An hour later strain. Use the decoction daily.
- Broth chamomile pharmaceutical - a valuable remedy for inflammation. Per liter of water - 1 tbsp. l colors. Zaarte, let it brew for 30 minutes, strain. Perform the procedure in the morning, afternoon and bedtime.
- Tatarnik prickly. Excellent relieves inflammation. Crush the leaves, pound, put gruel on the eruption sites. Hold 30 minutes.
- Armbands with woodruff fragrant. Coat fresh leaves cover ulcers. Perform the procedure 2 times a day.
- Dandelion infusion. Roots, leaves, rinse, chop, 2 tbsp. l raw materials pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, boil for 10–15 minutes. Present for half an hour strain the strainer. Drink a quarter cup 3 times a day.
- Decoction of burdock. Pour a spoonful of chopped root with 0.5 liters of water. Boil 10 minutes, let it brew for an hour, strain. Take a healing decoction twice a day before meals.
- Effective applications. Prepare a decoction: pour 2 tbsp. water 200 g of wild rose berries, the same amount of viburnum, add 100 g of nettle, 10 g of green walnut shells. Keep on fire for 10 minutes. Decoction infused day. Mix 50 g fresh cottage cheese and honey. Dilute cottage cheese and honey mixture with broth, make applications 3 times during the day for 15–20 minutes.
If the lesion is large, then antimicrobial drugs are prescribed orally - Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Cefalexin, Amoxicillin. Before using any of these funds, consult your doctor!
During treatment, avoid contact with water, do not visit the sauna, swimming pool or shower.
Dieting is not necessary when folliculitis occurs. But there are concomitant diseases in which the adjustment of the diet is necessary. Patients suffering from obesity or diabetes should follow a low carb diet.
It is important to adhere to the following rules in the diet:
- Consumption of animal fats should be limited.
- Avoid flour products, spices, chocolate, sweets, alcohol, strong coffee and tea from the diet.
- Eat as many fresh vegetables as possible to provide your body with the necessary amount of fiber. You can also eat bran.
- It should be included in the diet a sufficient amount of protein, including animal origin. Preference should be given to lean types of meat, such as veal, chicken and turkey.
- It is worth eating more foods rich in vitamins. Especially useful to be carrots, beets, rosehips, blueberries.
What is a folliculitis
That such a disease exists, few know. Very often it affects people of certain specialties, for example, miners, miners, locksmiths, oil workers, because there are all the prerequisites for the development of pathology. But almost no one is immune from this disease.

The inflammatory process affecting the hair follicles leads to the development of folliculitis, which requires mandatory treatment.
Folliculitis on the skin is a purulent inflammatory process in the upper sections of the hair follicle.. A papule forms more often pink in color, in the center of it an abscess is gradually formed, through which the hair passes. If the pathology is formed on the face or other parts of the body, but not on the head, then the hair may not be visible.
The whole process of pathology development takes several days, and then a crust forms, which most often disappears on its own.
Need to know. If you do not eliminate the factors that provoke the development of folliculitis, the disease can turn into a chronic form.
Folliculitis belongs to the pyoderma group, which is most often caused by staphylococci, fungi and some viruses.
Provocative factors of the disease
Inflammation of the hair follicle can occur for various reasons. To begin treatment, you need to find out what caused the disease. Most often provocateurs can be:
- Violation of the integrity of the epidermis after shaving in men, epilation, mechanical injuries.

Many women, caring for themselves and achieving a perfect smooth skin, and do not suspect that they can trigger the development of skin pathology
- Long stay in high or low temperatures.
- Violation of personal hygiene.
- Weak immunity.
- Hyperhidrosis.
- Chronic poisoning.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals.
- Increased sweating.
- The presence of dermatitis or eczema.
You can also call the risk factors that can increase the likelihood of inflammation of the hair follicle:
- Diabetes.
- Diaper rash in folds (most often occur in hot climates).
- Use of corticosteroid drugs.
- Therapy with antibacterial agents.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Exposure of chemicals to the skin, such as lubricants, kerosene.

Continuous exposure of the lubricant to the skin leads to blockage of the pores, which can lead to an inflammatory disease of the hair follicles.

Classification of pathology
Depending on the severity of the lesion, staphylococcal folliculitis is divided into two forms:
- Surface shape: osteofolliculitis, superficial folliculitis, decalvating folliculitis.
- Deep folliculitis: furuncle, carbuncle, undermining Hoffmann's folliculitis.

With deep forms of folliculitis, after treatment, scars remain on the skin.
Staphylococcal folliculitis is usually located on the chin, around the eyes. Often affects men who release a beard and mustache.
There is another classification of this disease according to etiology:
- Fungal folliculitis often provoked by fungi of the genus Candida. It can be localized on the shoulders, back, sometimes on the face and neck.
- Viral. It is often found in men on the chin and in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
- Syphilitic. It is often located on the scalp, in the region of the beard and mustache in men.
- Parasitic.
- Pseudomonad. It often develops after a hot bath, if the water is not sufficiently chlorinated. May affect patients who are undergoing acne treatment with antibiotics.
We treat folliculitis drugs
If the disease is mild, you can do with local drugs., eg:
- For staphylococcal folliculitis, treat the affected areas with antibacterial ointments, for example, Mupirocin. This should be done 2 times a day.

If the pathology is provoked by staphylococci, then one cannot do without antibacterial agents.
- If the disease is caused by Gram-negative bacteria, use of benzoyl peroxide is indicated topically.
- Herpetic folliculitis can be treated with Acyclovir ointment.
- In any form of the disease, apply local antiseptics, for example, Fukortsin, Chlorhexidine.
Need to know. To prevent the spread of infection to healthy skin, it is necessary to process them with boric or salicylic alcohol.

In the presence of folliculitis, it is necessary to treat adjacent areas to prevent the spread of pathology.
If the treatment of inflammation of the hair follicle is not amenable to treatment with local means, then you will have to resort to taking antibacterial drugs orally.
Antibiotics are also prescribed if:
- The disease has become chronic.
- There is inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- The process quickly spreads to adjacent areas.
If the infection is caused by staphylococcus, then prescribe:
- Cephalexin up to 4 times per day.

Staphylococcal folliculitis will not be able to win without modern antibacterial agents
- Erythromycin.
- Minocycline if Staphylococcus is resistant to other medicines.
Pseudomonadal folliculitis, occurring in a severe form, requires taking Ciprofloxacin 500 mg 2 times a day.
When fungal folliculitis is prescribed inside:
The drug is selected depending on the type of bacteria. In case of herpetic folliculitis, antiviral agents are prescribed inside.
Any treatment must necessarily involve the elimination of a provoking factor, for example, if diabetes mellitus aggravates the course of the folliculitis, then it is necessary to conduct its therapy.
In severe pathology, systemic therapy is required.
Need to know. Any form of folliculitis during therapy requires to exclude washing of the affected areas with water and taking hot baths.

During treatment, it must be remembered that a hot bath can complicate the course of the inflammatory process.
Physiotherapy treatments
Physical therapy can significantly help in the treatment of folliculitis. Physiotherapy has the following effects:
- Remove the inflammatory process.
- Inhibit the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Increase immunity.
- Activate the formation of vitamin D in the skin.
The following methods are most commonly used:
- Exposure to lesions with short ultraviolet waves.
- General UFO.
- Low-intensity UHF therapy.
- Laser treatment.

Physiotherapy will be a great help in treating folliculitis. Her methods will accelerate healing, relieve inflammation.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Dry warm.
Use of traditional medicine
Hoffman's folliculitis and other forms can be treated using traditional remedies, but they should complement the basic drug therapy and be sure to be coordinated with your doctor.
The following recipes have proven effective:
- Application of chamomile decoction. It relieves inflammation perfectly.

Chamomile is distinguished by its antiseptic properties, so its decoction can be safely used for washing in the presence of any inflammatory lesions on the skin.
- Inside you can take a decoction of burdock root or dandelion. To prepare the medicine, you need to take a tablespoon of raw materials and pour 0.5 liters of water, boil for 10 minutes. After 2-hour infusion, take 50 ml 2 times a day.
- For compresses on the affected areas you can use the leaves of the thistle, unfortunately, this method can be used only in the summer. The leaves must be crushed and applied to the inflamed places.
- For compresses, baths and dressings, you can use a decoction of the root of the thistle. To make it, you need 50 grams of dry raw material, pour half a liter of water and boil over low heat for 30 minutes, and then infuse for 2 hours.
Prediction and prevention of the disease
Most often, it is completely possible to completely defeat the disease if therapy is started in a timely manner. If there is a deep folliculitis, then scars and pigmentation sites may form at the site of the abscess..
If the therapy is chosen correctly, then it is possible to cope with the pathology in a few days. But the lack of effective treatment and non-compliance with the recommendations of the doctor is fraught with the development of complications:
- Furunculosis.
- Abscess.
- Lymphadenitis.
- Folliculitis can result in scalp dermatophytosis.
- The most serious complications include meningitis..
To preventive measures include:
- Personal hygiene.
- Proper selection of skin and hair care products.

For the prevention of skin diseases it is very important to choose the right hair and skin care products.
- Use special cosmetics during shaving.
- Use antiseptic when even small abrasions and damages appear on the skin.
- Do not abuse the antibacterial soap, it not only kills pathogenic bacteria, but also breaks the protective barrier.
- To carry out timely treatment of diseases that can trigger the development of folliculitis.
Any disease is easier to treat at the very beginning of the development of pathology. This directly concerns the folliculitis. Treatment should be selected by a specialist taking into account the cause of the disease, then the effectiveness of therapy will be 100%.
Clinical picture
 The general signs of the disease are caused by the properties of the staphylococci themselves. In the center of the pustules often appear hair. These formations have a hemispherical or conical shape and thick walls.
The general signs of the disease are caused by the properties of the staphylococci themselves. In the center of the pustules often appear hair. These formations have a hemispherical or conical shape and thick walls.
With a superficial folliculitis, the wound looks like a small vial with a bright red rim. In the center of the lesion is a hair. The development of the disease begins with increased sensitivity and redness of the skin, then swelling occurs. After a few days, the contents of the abscess disappear, and its surface dries out. Superficial folliculitis is often localized to the hips, neck, legs, forearms, and face.
A deep type of ailment implies penetration of harmful microorganisms deep into the bulb. At the same time, nodules appear at the beginning of the hair, turning into ulcers. After a week and a half, the bubble dries out, leaving behind a small scar. Often, lesions are observed on the neck and scalp.
Chronic folliculitis is usually accompanied by the regular appearance of new formations. The disease often occurs in places prone to permanent injury and friction.
Treatment methods
As for the treatment of folliculitis, it must be complex and include:
 dietary adjustment
dietary adjustment- hygiene,
- treatment of the affected skin with antiseptic preparations,
- the use of drugs for internal use and local drugs
- physiotherapy,
- phytotherapy
- treatment of concomitant diseases.
 Treatment of folliculitis is determined by a dermatologist. Self-treatment in this case can not only become ineffective, but also lead to more serious complications.
Treatment of folliculitis is determined by a dermatologist. Self-treatment in this case can not only become ineffective, but also lead to more serious complications.
Folliculitis on the back is preferably treated with antiseptic solutions: salicylic alcohol, boric acid and potassium permanganate. Use and local preparations, for example, antibacterial creams.
Home treatment can be combined with herbal medicine. The face should be cleaned with tincture of plantain, St. John's wort, and elecampane. Birch leaves can be used for making tinctures for washing.
The consequences of untimely or improper folliculitis treatment - The development of infection in the deep layers of the epidermis with the formation of an abscess, carbuncles and boils. These diseases can be dangerous not only for the health of the patient, but also for his life. Therefore, folliculitis under the arm or in some other place should be treated on time, not forgetting about preventive measures.
Types, forms and stages
 The classification of folliculitis depends on the grounds by which the types of disease are distinguished.
The classification of folliculitis depends on the grounds by which the types of disease are distinguished.
Depending on the cause of the inflammation process:
- bacterial,
- fungal,
- syphilitic,
- parasitic,
- viral.
According to the degree of skin lesions:
- superficial folliculitis - small-sized abscesses form on the skin, which become crusted over two days,
- deep inflammation of the follicles - very painful pustules form on the skin, which become crusted for five days.
According to the presence of complications of the development of the inflammatory process:
Symptoms and signs
Alert about the development of the inflammatory process of the hair follicle may following symptoms:
- redness around the hair with the further formation of an abscess,
- infiltration and pus in the pustules,
- spherical or cone-shaped inflammation of the skin,
- enlarged lymph nodes
- itching and redness of the skin, persisting after the opening of the abscess.
At the first signs of inflammation, you should consult a dermatologist. Only timely medical consultation and well-chosen treatment provide a guarantee of full recovery.
Be careful! Ignoring the problem can cause the development of severe complications of folliculitis: boils, abscesses, follicular scars.
Treatment methods
Treatment of folliculitis complex, involves the use of the following methods:
- Physiotherapy procedures. It is possible to intensify the process of restoring damaged tissues and prevent the development of inflammation in healthy areas of the skin using the UV-irradiation method.
- Traditional methods of treatment. Well treat the affected skin with fresh plantain juice or chamomile broth. Inside take a decoction of dandelion. For 50 g of dry material you need to take 200 ml of boiling water. Dry leaves steamed, insist and take over the day on a tablespoon.
- Drug therapy. Depending on the microorganism that caused the inflammatory process, the patient is shown the following medications:
- Erythromycin, Methicillin - with staphylococcal folliculitis,
- Terbinafine or Itrakanazol - with fungal infections,
- Acyclovir - with inflammation of the herpetic type.
Simultaneously with taking the pills, the affected area is treated with antibiotic ointments. Supportive drug therapy - taking vitamin complexes, immunostimulating drugs.
Preventive measures
Adhering to the elementary rules of prevention, it is possible not only to speed up the healing process, but also to prevent the development of the inflammatory process in the future:
- Carefully observe body hygiene.
- Do not wear skin-thinning clothing.
- follow the rules of protected sex,
- strengthen immunity (healthy eating, giving up bad habits),
- monitor your health and, if necessary, consult a doctor in a timely manner,
- as far as possible limit contact with chemical toxicants.
The prognosis for the complete elimination of folliculitis is favorable. But only under the condition of timely treatment to the doctor, competently carried out treatment and compliance with the rules of prevention.
Useful videos
Candida folliculitis: symptoms and diagnosis of the disease, especially treatment and prevention.
What is the folliculitis of the hairy part of both the head and the body.

 dietary adjustment
dietary adjustment

